Process Optimisation
Map Reality, Model Improvement, Close the Gap.
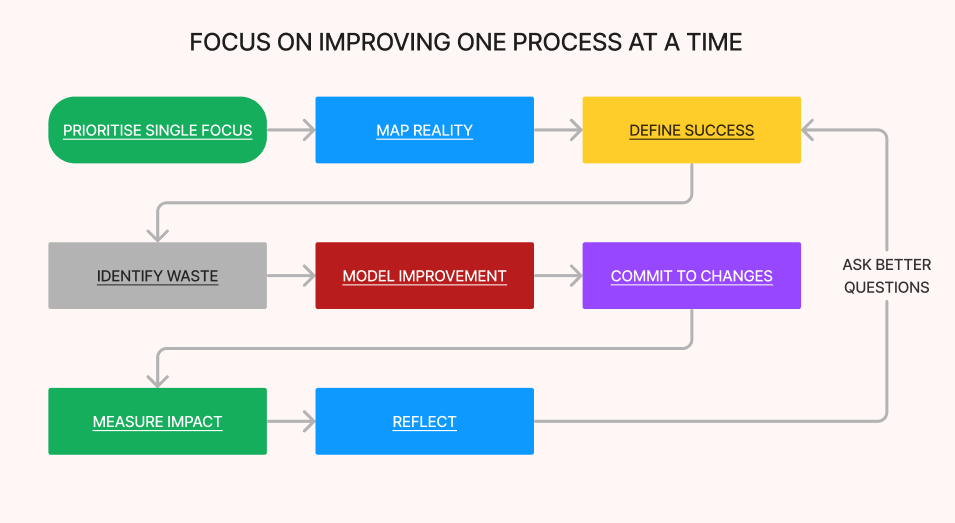
Make it easy to do the right thing and annoying to do the wrong thing.
Purpose
Build trust in systems that operate more effectively to transform and distribute value through embedded situational wisdom.
- Build Trust
- Better Quality
- Greater Capacity
- Faster Cycles
Principles
This section covers the methods for capturing, measuring, and improving processes. For terminology definitions, see Naming Standards.
Four levels, from strategic to tactical:
STANDARD (Glue) → PROCESS (Tacit) → PROCEDURE (Explicit) → WORKFLOW (Trace)
| Level | Term | Concept | Definition |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Standards | Atoms and Bits of interoperability and composability | The Ontology (Why things relate) |
| 2 | Process | Process Knowledge | The Goal (What needs to happen - Tacit) |
| 3 | Procedure | Procedural Knowledge | The Rules (Formalized logic - Explicit) |
| 4 | Workflow | Decision Trace | The Execution (How it actually happened) |
Full definitions: Naming Standards → Operations Terminology
Processes
Work Charts vs. Workflows, different tools for different questions:
| Tool | Question | Maps |
|---|---|---|
| Work Chart | Who does what? | Capability → Demand |
| Workflow | How is it done? | Steps → Outcome |
They work together:
- Workcharts identify WHAT activities exist and WHO does them
- Workflow documents HOW each activity is performed
Process Maturity
Track where each workflow sits:
| Status | Symbol | Definition | Next Step |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gap | GAP | No documentation exists | Document the workflow |
| Draft | D | Documented but not validated | Test with real work |
| Failing | F | Documented but not working | Diagnose and fix |
| Approved | A | Validated and approved | Monitor performance |
| Needs Work | NW | Approved but degrading | Schedule review |
| Active Review | AR | Currently being improved | Complete review cycle |
Audit Questions
For each process, ask:
- Is this process common to all businesses?
- What is the current state? (Use symbols above)
- What triggers the process?
- Who owns it?
- How do we know it's working?
Triggers
What initiates a workflow?
| Trigger Type | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Schedule | Time-based recurrence | Weekly content calendar |
| Event | Something happened | New lead captured |
| Threshold | Metric crossed a line | Bounce rate > 70% |
| Request | Someone asked | Customer support ticket |
Document triggers in every workflow — if you don't know when to run it, it won't get run.
Workflow Structure
Every workflow document should include:
1. Overview
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
| Purpose | What outcome does this produce? |
| Trigger | What initiates this workflow? |
| Frequency | How often does it run? |
| Duration | How long does it take? |
| Owner | Who is responsible? |
| Output | What gets produced? |
2. Prerequisites
- Tools required
- Access requirements
- Knowledge requirements
3. Inputs
What you need before starting.
4. Process
Phased steps with checklists at each phase.
5. Outputs
What gets produced, in what format, delivered where.
6. Success Criteria
How to know it's done right — quality metrics and performance metrics.
7. Failure Modes
Common problems and their solutions.
Reference implementation: Article Copywriting Workflow
Improvement Methods
Process Mapping
Visualize the current state before improving.
- See the big picture and the details simultaneously
- Identify bottlenecks, redundancies, gaps
- Create shared understanding across team
More: Process Mapping
Process Modelling
Simulate changes before implementing.
- Test hypotheses about improvements
- Quantify impact of changes
- Reduce risk of failed changes
More: Process Modelling
Quality Assurance
Ensure consistent outcomes.
- Define acceptance criteria
- Build verification into workflows
- Create feedback loops for improvement
More: Quality Assurance
Checklists
The simplest, most powerful improvement tool.
- Reduce errors and oversights
- Improve consistency
- Enable delegation without loss of quality
Types:
- Do-Confirm: Complete tasks from memory, then verify against checklist
- Read-Do: Read each item, then do it (for unfamiliar or high-risk work)
More: Checklists
The Improvement Loop
DOCUMENT → MEASURE → ANALYZE → IMPROVE → STANDARDIZE
↑ |
└─────────────────────────────────────────┘
- Document — Capture current state as a workflow
- Measure — Track performance against success criteria
- Analyze — Identify gaps between actual and desired
- Improve — Change the workflow to close gaps
- Standardize — Update documentation, train team
Repeat continuously.
Process ↔ Context
Process and context shape each other. Neither is primary.
PROCESS (Yang) CONTEXT (Yin)
───────────── ────────────
How we proceed Why this time
Creates movement Creates meaning
Repeatable Situational
───────────────────────────────────────────────
↓ ↓
Execution creates Traces reveal
decision traces patterns
↓ ↓
Traces become Patterns improve
queryable context process
└──────────────────────────────┘
Process without context = Bureaucracy. Following steps without knowing why. Context without process = Chaos. Knowing why but no repeatable path.
Example: A support team has a process for escalations. First month, they escalate 40% of tickets—no context on what worked. By month six, decision traces show which escalations resolved fastest. The process tightens. Escalation rate drops to 15%. Context improved process. Process generated better context.
Together they spiral upward. Each cycle adds to the context graph.
Anti-Patterns
| Anti-Pattern | Problem | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Undocumented | Knowledge locked in heads | Document as workflows |
| Over-documented | Nobody reads 50-page SOPs | Keep workflows scannable |
| Never updated | Documentation drifts from reality | Review triggers, scheduled audits |
| No metrics | Can't tell if it's working | Define success criteria upfront |
| No owner | Nobody responsible for improvement | Assign ownership |
| Too rigid | Can't adapt to context | Build in decision points |
| Too loose | Inconsistent outcomes | Add checklists at critical points |
Subsections
- Checklists — The power of verification
- Process Mapping — Visualizing the current state
- Process Modelling — Simulating before changing
- Quality Assurance — Ensuring consistent outcomes
Context
- First Principles — Question requirements before optimising them
- Standards — Where improved processes compound into predictability
- Naming Standards — Canonical terminology
- Work Charts — Who does what (capability → demand)
- Marketing Activities — Reference implementation
- BOaaS — Business Operations as a Service