Product Engineering
Transform Problems into Products.
Great products deliver great outcomes. What annoys you? What needs to be done? How can you help others fall into a pit of success?
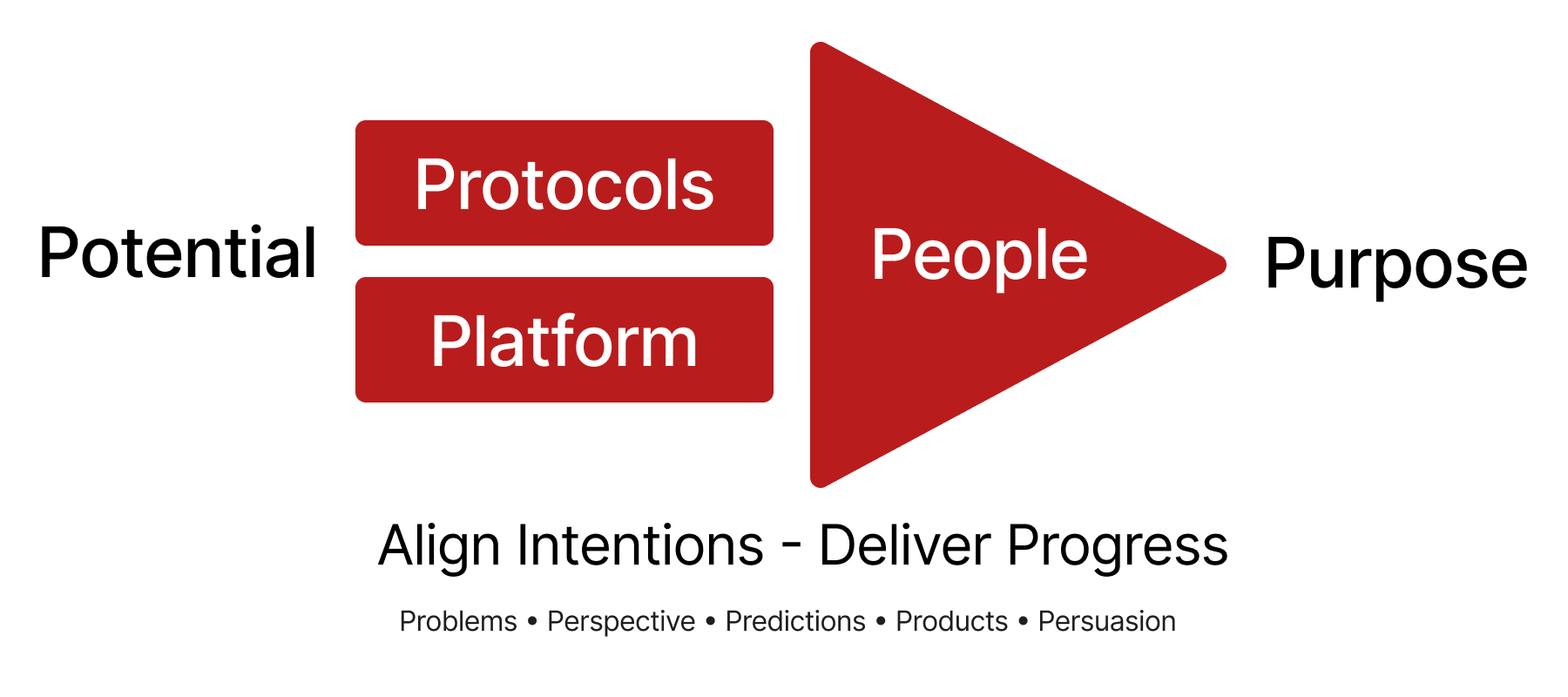
Your platform is your most valuable product
Flow
We have a problem, and I am not 100% sure what succcess look in the frontend interaction - what do I put it in, what should I expect as a valuable return, how will I qualify quantify that, and how long should I wait or pay (attention or money)
Subject Matter
Engineer systems that make it impossible not to follow the critical path to success.
- Jobs To Be Done
- Expectations vs Outcomes
- Market Research
- Delivery Playbook
- Product Distribution
- Developer Experience
Picture Success
1. What Should Happen in the Frontend Interaction?
A. User Journey (Ideal Flow):
User enters a research topic and (optionally) clarifications. User clicks “Start Deep Research”.
UI shows a status/streaming region:
- “Retrieving and generating…” or similar status.
- Any errors are shown here, clearly and accessibly.
UI shows findings as they stream in:
- Each finding includes a summary and a source/citation.
- User can filter findings by source type (web, internal, pdf, etc).
UI shows the final report:
- The report includes inline citations and a source appendix.
- All content is accessible (screen reader/keyboard friendly).
B. What Should You Expect as a Valuable Return?
At a minimum:
- A status update (so the user knows work is happening).
- At least one finding (with summary + source).
- A final report (with citations and appendix).
Bonus:
- No errors, or if errors occur, they are clearly shown and actionable.
- The UI is responsive and does not “hang” or leave the user guessing.
2. How Will You Qualify/Quantify Success?
A. Qualitative:
The user sees clear progress (status updates, streaming findings). The user can always see what’s happening or what went wrong. The report is readable, cited, and actionable.
B. Quantitative:
- Time to first result:
- User sees a status message within 1 second.
- First finding appears within 2-5 seconds (for mocked/tested flows).
- Completeness:
- At least 1 finding and a final report are always produced, or a clear error is shown.
- No unnecessary API costs:
- All tests and most dev flows use mocks, not real external APIs.
- Accessibility: All interactive elements are keyboard and screen reader accessible.
3. How Long Should You Wait or Pay?
In development/test:
Everything should be instant (mocked). If you wait more than 5 seconds for a response, something is wrong. In production: User should see status within 1 second, first finding within 5-10 seconds. If it takes longer, show a “still working…” message and allow the user to cancel or retry.
Cost:
Never pay for real API calls in tests or dev.
In production, track API usage and warn if requests are unusually slow or expensive.
4. How to Avoid Wasting Time, Money, or Attention
Use mocks for all tests and most dev work.
Show status and errors in the UI at all times.
Set timeouts for API calls and show fallback messages if things take too long.
Log/report API usage and errors for later review.
Prove Demand
Put yourself in the customer's shoes. Walk their journey with them, observing emotional triggers and quantifying estimates where value is lost.
What do all people need?
- Safe and Clean Environment
- Water and Nutritious Food
What makes life enjoyable?
- Play
- Freedom
- Happy Memories
Qualify Value
- Convert stories into worksheets linking back to the transcribed conversation.
- Proportion stories to ledgers as appropriate
- Link aggregated stories to a cashflow forecast for each ledger item.
- Allocate specific revenue streams to a dedicated ledger
- Proportion feature benefits to a revenue stream
- Proportion waste eliminating tasks to expense ledgers
- Proportion sustaining expenses
Quantify Expected Rewards Link JTBD improvement stories to potential progress in value ledger and belief system.
- Lost opportunity
- Lost time
- Cost of errors
Who needs a solution?
- Addressing Pain or Performance
- Time horizon? Urgent or Future
- Who cares the most?
Price is what people will pay; Value is what you deliver.
- What is the DCF on a feature idea?
- Do you have the resources?
- Do you have the hunger?
The Pit of Success
Make it impossible to fail.
What makes people tick?
Where does friction get in the way?
- Falling into the Pit of Success
- How to Fail at Almost Everything and Still Win Big
- Don't Make Me Think
Progress Journey
Use reflective listening to capture stories that resonate with emotions.
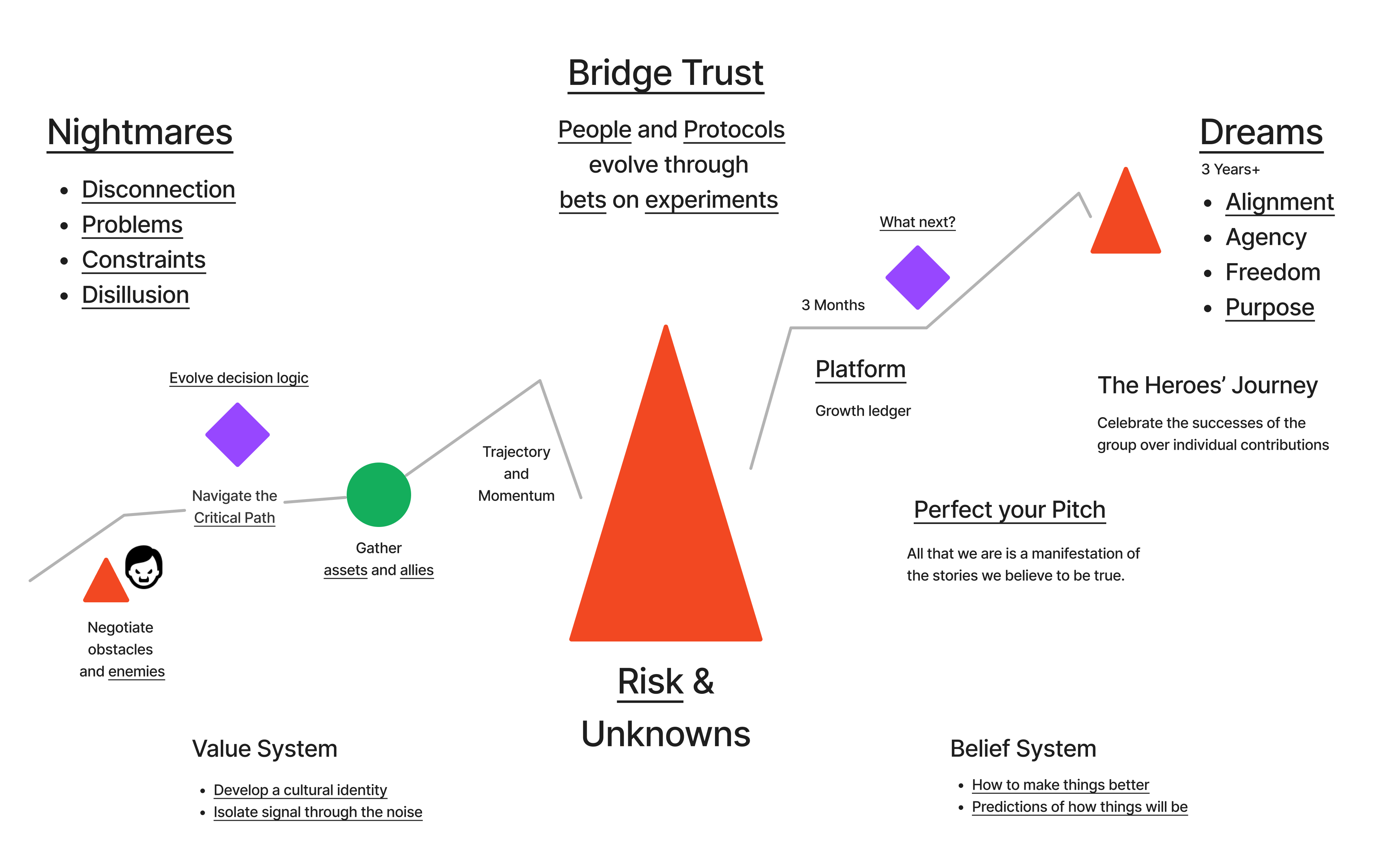
- Focus on the agents/customer's context, required actions, and desired outcomes.
- Conduct story-based customer interviews
- Map the customer's full decision journey
- Understand the three key motivations driving customer progress
- Recognize that every decision has a cause, not a random walk
- Shift from a selling mindset to a helping mindset
Design and Mind
Use human centred design to reduce cognitive load in making progress.
Seven, Plus or Minus Two. Don't overload the brain with too much information when making presentations.
Simplify Choices
Decision Architecture is a field of study and practice that focuses on the design of choices and decision-making processes. It involves the systematic organisation and structure of information, options, and feedback to influence and guide people's decisions towards desired outcomes.
Choice architecture manipulates the context in which people make decisions. Our choices are influenced by factors we are not consciously aware of: different people can arrive at different decisions based on minor differences in how options are framed, what the default option is, and how their surrounding environment primes their mindset.
Engineer systems that provide the freedom to focus of high value decisions
Expected Reward
Use Outcome Driven Design to create a clear definition of what success looks like, then work backwards to dream up the path to get there.
Customer Success:
- What does success for the customer look like?
- How can you measure success?
- How will you know if you are off course?
Business/Product Success:
- Positioning
- Pricing
- Constant and honest revision of cost and effort estimates is important to avoid over-investing in unviable ideas.
- Dynamic cost assessment helps in making rational decisions throughout the development process.